Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
what exactly is PBL?
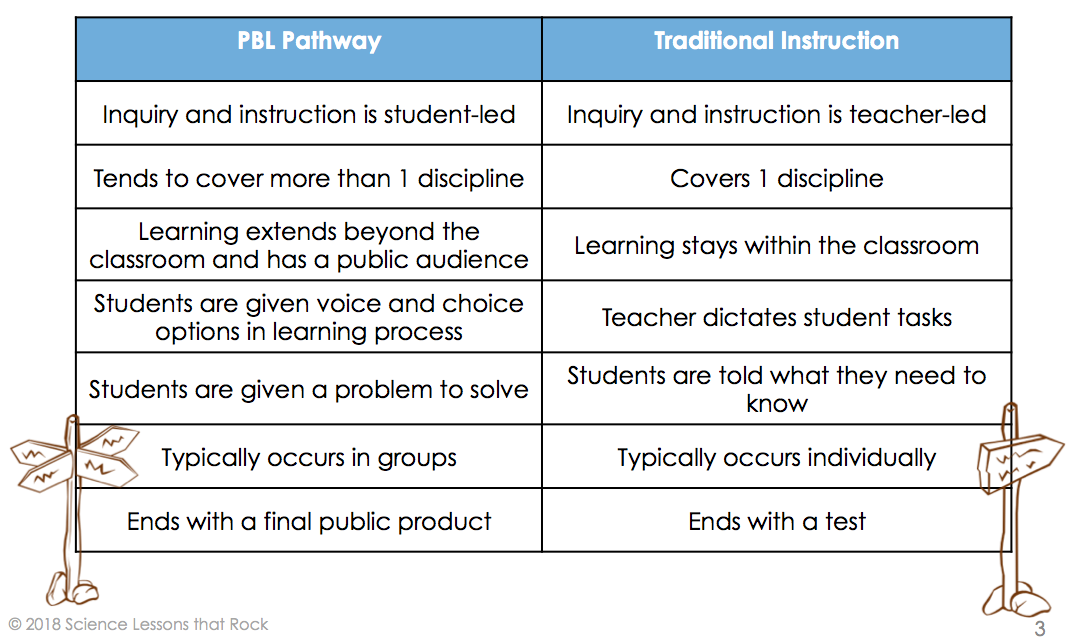
Project based learning is much different than just throwing a project into your curriculum. Project based learning is a shift in the entire way you teach and run your classroom. Take a look at the chart below that compares project based learning with traditional classrooms:
Why choose PBL?
Imagine a classroom where students are truly engaged in the content, they feel like the concepts are applicable to their lives, and they have to use critical thinking skills on a daily basis in order to solve a problem. Project based learning can take that student who usually zones out in class and turn him or her into a leader. When you choose the right topic, it brings your content to life and students feel like they have ownership over their learning. I’m currently in my 3rd year teaching PBL, and I’ve seen engagement skyrocket. Not only that, but learning goes much deeper. In PBL, students solve a real problem, opposed to doing a traditional project like build a model of a cell that doesn’t require any critical thinking.
One criticism of PBL…
One thing that students might complain about is that the majority of the PBL process is done in groups. If you have a student that doesn’t like working in groups then they might complain. One way to combat this problem is:
- Always have a group product and an individual product to grade. That way students aren’t completely relying on their group members to get a good grade.
- Create team roles that work with everyone’s strengths. Not everyone likes to be creative, just like not everyone likes to write or use technology. For example, you might have a project where students need to create a cookbook. You can have one student research the recipes and nutritional content. The second student might be in charge of cooking the recipe and taking pictures. A third student might like computers and wants to put the electronic cook book together and edit. If you pick diverse team roles then everyone should have a role that they are comfortable with.
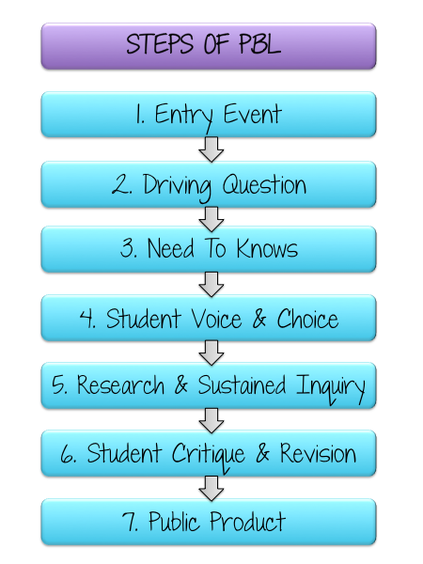
What are the steps of PBL?
Project based learning occurs in 7 main steps. In the next blog post, I will cover the entry event, driving question, and student need-to-knows. In the 3rd blog post, I will talk about the meat of the project- creating the product and all that comes with it. In the last blog post I will discuss why it is so important to have a public audience and build community partnerships.
Before you continue, there are 2 words you need to know so you don’t get confused. The words “project” and “product” mean very different things in the PBL process.
The PROJECT is the overall process of PBL that includes the 7 steps listed above. It is everything needed to complete the process from start to finish.
The PRODUCT is what students create at the end of the project to demonstrate their learning. It might be an essay, a cookbook, a podcast, or a fundraiser.